We have already covered a series of episodes where we are setting up our Linux server to work with a netcore application. But to deploy the application, we need to upload the files to our server, so we will create an FTP server.
To follow these steps you must be connected to your server via ssh and use a user with sudo privileges.
Table of Contents
1 - Enable the EPEL Repository
First of all, we can update our system using (this is optional):
sudo yum -y updateKeep in mind this command will update all installed packages.
The reason we will enable the EPEL repository is so we can install a wide variety of open source packages using the yum package manager.
In our case, we are looking for the ProFTPD package, which is simple, secure, and easy to configure.
To enable the EPEL repository, run the following commands:
$ sudo wget https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/7/x86_64/Packages/e/epel-release-7-11.noarch.rpm
$ sudo rpm -ivh epel-release-7-11.noarch.rpmAnd to check if the repository is available, run the following command:
$ sudo yum repolist | grep epel
2 - Install FTP Server on CentOS
Once we have the repository, we only need a single command to install our FTP server:
$ sudo yum install proftpd proftpd-utils
3 - Start ProFTPD
Once we have the service installed, we just need to start it. To do this, run these two quick commands:
$ sudo systemctl start proftpd
$ sudo systemctl enable proftpd
4 - Verify ProFTPD Installation on CentOS
Technically, you can now connect to your VPS server using any FTP client you have, such as FileZilla.
As an example, for the host I used the IP 192.168.1.1, but you should enter the IP of your actual server, the same one you use to connect via ssh.
Now you have the ability to upload and download files from your server with no issues.
If you cannot connect, it's probably a port issue. See step 7 to learn how to open the necessary ports.
5 - Changes to the ProFTPD Configuration
If you make any changes to the configuration (you can see different configurations here), which are applied in the /etc/proftpd.conf file, keep in mind that these changes will only take effect after you restart the service. To do this, run the following command:
$ sudo systemctl restart proftpd
6 - Check the Log Files
If you have any issues, ProFTPD keeps a log of errors in the /var/log/proftpd directory.
Of course, you can quickly check the current status of the service by running:
$ sudo systemctl status proftpd
Common Errors
When we install our Linux server, by default security is very high, so port 21 (used for FTP connection) will be closed.
The first thing to do is check whether or not this port is closed.
To check, run the following command:
$ sudo iptables -nvLYou can check if the port is open or not. The information it shows might be a bit confusing, but generally it will look like this:
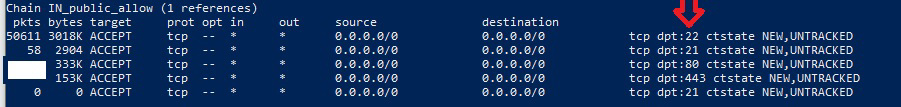
So you should open the port you are going to use (21 and 22).
7 - Open FTP Port in Linux
To open a port in Linux, simply run the following command:
$ sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=21/tcp
$ sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=ftpAnd if you also want to open the port for SSH, make sure to open port 22 as well:
$ sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=22/tcp
$ sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=ftp
Conclusion
We definitely need an FTP server to be able to upload our files to the server, and ProFTPD is a great option due to everything it offers in terms of configuration.

