In the past, I have shown on the channel how to make an API in .NET and currently I am creating a course about Blazor which will call this API for backend purposes.
In the real world, when we work with APIs we need to secure them, including adding security, so today we are going to see the most common way of implementing security in our APIs using JWT or JSON Web Tokens.
Before starting with the video, just to mention: we are not going to see how to implement JWT in code, but rather have a general overview of what JWT is, and this is applicable to any language.
Index
1 - What are security tokens for
To understand what a JWT is we need to understand what a security token is and what its purpose is.
As its name suggests, a security token is a token, which is a string of text that gives us information about the token. This information could be, for example, the issuer of the token, the lifetime of the token, maybe user rewards or the username itself, etc.
These tokens are usually signed symmetrically or asymmetrically, depending on the technology used, but the main idea is the same: to prevent modification or forgery of the tokens.
Therefore, security tokens are used to identify the user or client that is using the service.
2 - What is JWT (Json Web Token)
JWT is a popular (the most popular) security token format, which uses JSON but is encoded in base64 to make it easier to transfer and use over HTTP.
For this token to be effective, we send it in the HTTP request header as part of bearer authentication.
But it is not the only security token; there are also SAML or SWT tokens.
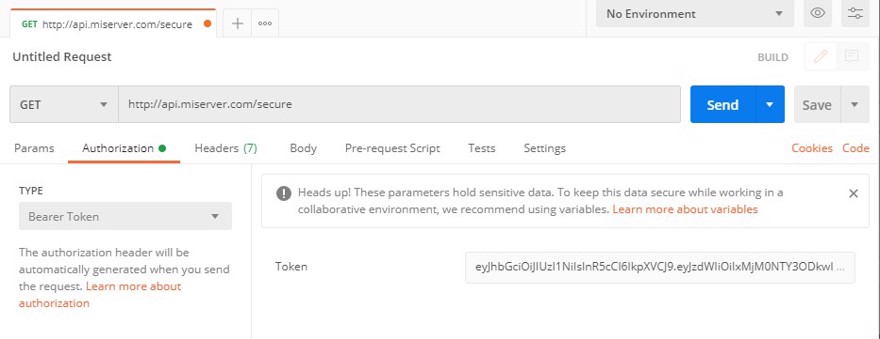
Note: Image using Postman where I show the Authorization
2.1 - Parts of a Json web token
As I mentioned before, we can include information in the token, such as username or permissions.
To explain the parts of a token, let's look at a simple example:
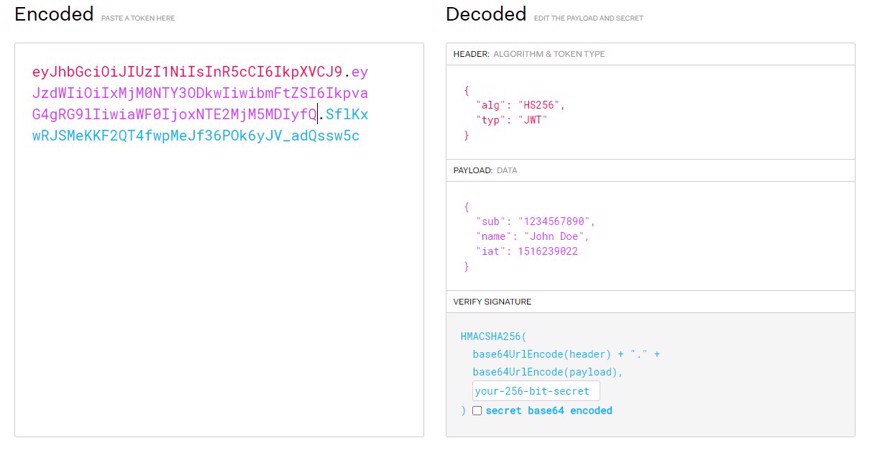
As we can see, it has different sections:
2.1.1 - Header
Contains the algorithm and the type of token
{
"alg": "HS256",
"typ": "JWT"
}
2.1.2 - Payload
Contains the data. Here we include the username, permissions, etc. In general, the information we want available; this is also commonly referred to as the "claims".
{
"sub": "1234567890",
"name": "John Doe",
"iat": 1516239022
}Note: This information is not encrypted, so anyone with access to the token can read it. Sensitive information such as passwords should not be included in the token.
2.1.3 - Signature
Finally, the area where the signature of the service that creates the token is included.
HMACSHA256(
base64UrlEncode(header) + "." +
base64UrlEncode(payload),
your-256-bit-secret
)
2.1.4 - Final result
We can also see the final result that we are going to receive, and as we can see, each of the three sections is separated by the period character.
eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9
.eyJzdWIiOiIxMjM0NTY3ODkwIiwibmFtZSI6IkpvaG4gRG9lIiwiaWF0IjoxNTE2MjM5MDIyfQ
.SflKxwRJSMeKKF2QT4fwpMeJf36POk6yJV_adQssw5c
3 - Difference between Authentication and Authorization
When we talk about JWT or permissions, the words authenticate and authorize always come to mind.
First, a short description:
Authenticate is the process of verifying the identity of a user, typically using credentials such as username and password.
Authorize is once we are authenticated, the process of checking if that user has permission to access the system.
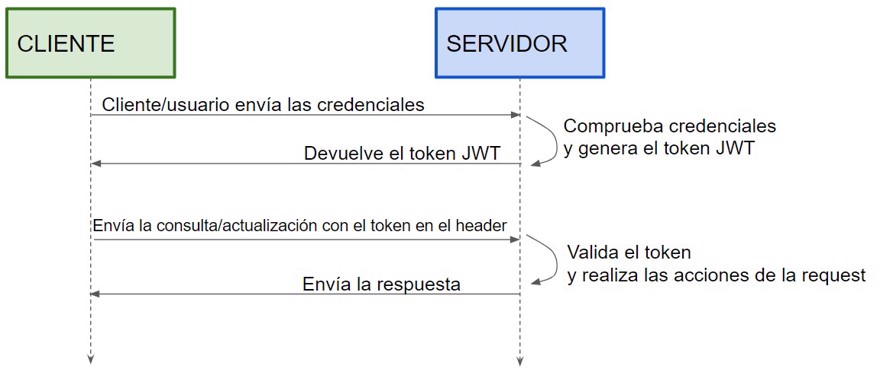
The authorization (and authentication) process can be managed by the same server as the authorization, or not. For example, it is common nowadays to delegate authentication to services such as Google or Facebook. (It's typical on websites to see "login with Google"). And that's where OAuth comes in.
3.1 - What is OAuth?
OAuth is a standard for authorization and anyone can implement it.
That's why I mentioned that it can come from our own server or from another, such as Google.
3.2 - What is OAuth2?
As you might imagine, it's the version 2 of the OAuth protocol. It simplifies the previous version and makes its use between applications easier.
As mentioned above, the great advantage of using OAuth is that we delegate authentication and authorization of our users to third-party services (like Google or Facebook).
This functionality is very useful for many websites, since sometimes they only need the username, for example, to comment on a post.
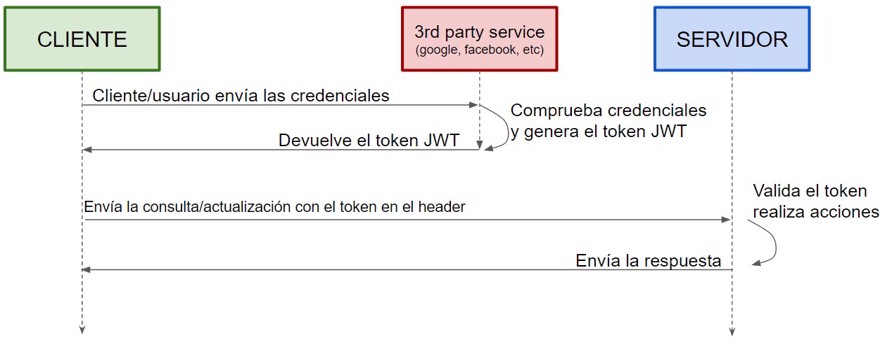
4 - Differences between JWT and OAuth
At this stage, we are clear on the difference between JWT and OAuth (or OAuth2).
JWT is the format of the security token, while OAuth is the standard authorization protocol that can use JWT as a token.
In a real use case, we shouldn't worry about how a user got that token, just that when they come to our application we should validate it and if it's valid, process the request. However, to logout or end the session we need to use OAuth2, since JWT by itself can't "cancel the token"; it just has an expiration time and the token will be valid until it expires.
5 - Using JWT in microservices
When we are working with microservices, using JWT is very common. Within the same microservice or application, you can call different services without having to login each time.
Imagine an application, fairly large, where we have access to information about movies, actors, series, each of them being a microservice.
At the end of the day, a microservice is an application that is fully functional on its own, so if you need certain permissions to access that information, you must be identified in the system.
However, if we think about it, it doesn't make much sense to ask the user to log in three times; once should be enough. This is where JWT comes in.
Whether it is in our own server or in a third-party one, we login, and it will return a token. And we’ll use that token to query or request information from the different services.
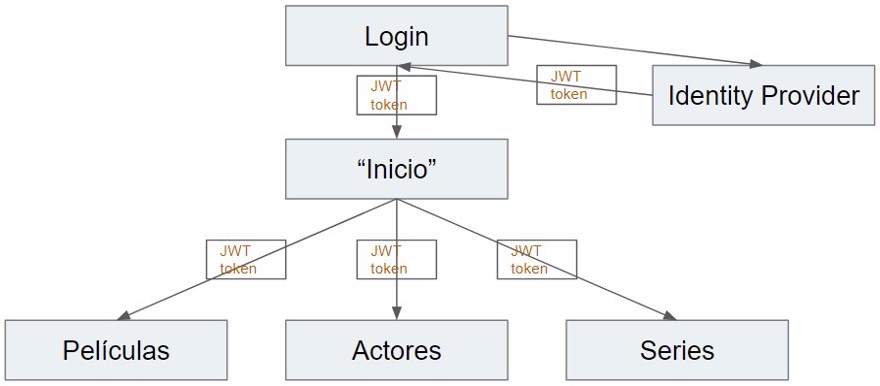
The token we usually receive is of type bearer token, to help prevent CSRF (cross site scripting) in our requests.
6 - Advantages and Disadvantages of json web tokens
6.1 - Advantages of JWT
JWT tokens are what are known as stateless, they are not stored on the server side so they do not consume memory.
With the JWT signature we ensure their origin and validity, which allows us to trust that the request is legitimate.
The same token can be used for multiple applications, which can sometimes improve the user experience and, of course, development.
6.2 - Disadvantages of JWT
For me, the biggest disadvantage of JWT is that since a token is valid for X time, if we want to logout or as administrators deny access to a token that already exists, we have to wait until the token expires or implement additional mechanisms like blacklists which add a lot of complexity to the system.
(For example, if a token has been stolen)
As I mentioned throughout the post, tokens are valid for a certain period of time, but what happens if the time runs out and we want to remain logged in? For that we need to implement what are called Refresh tokens, which allow us to refresh tokens so that they remain valid.
Conclusion
In this post, we've seen what JWTs are and what they are used for, as well as Oauth/Oauth2
The differences between JWT and OAuth
How JWT is used in microservices and what the advantages and disadvantages of JWT are.


