Index
1 - What is cherry pick in git?
Cherry pick is a Git feature that allows us to take a commit from one branch and apply it to another branch.
When we do a cherry pick, we do it with a single commit, while if we do a merge or rebase, the action is performed over several commits.
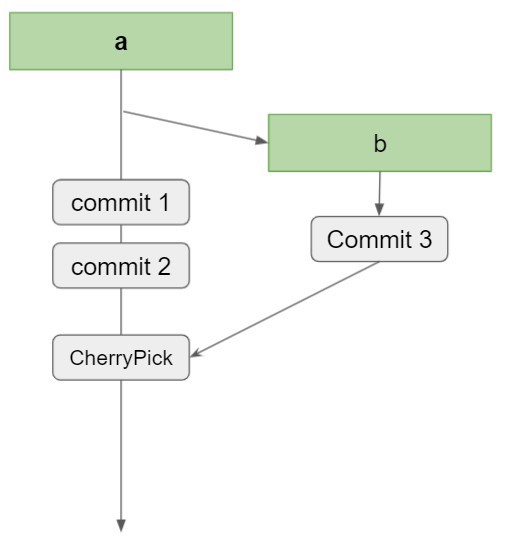
2 - When to use cherry pick in git?
Before we continue, we must be clear that the cherry pick feature is very useful in certain scenarios, but in others it can be quite confusing, as it can generate duplicate commits, which will cause massive conflicts.
2.1 - Hotfixes to fix bugs
The main use is when we have hotfixes. A hotfix is basically a change that we must put into production no matter what, since it is going to fix a bug.
This kind of action is very common when we have a release branch. Let’s say we discover a critical bug, fix it, and merge it to master. At the same time, we need to apply it to the branch that is currently in production.
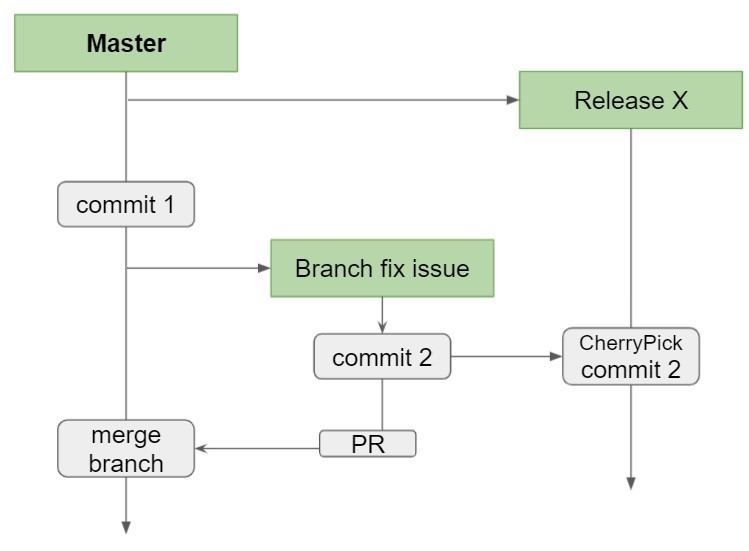
Another common case is when the developer finds a bug while working on another feature, so they create a single commit to fix the bug and also cherry pick this commit into the branch in production.
2.2 - Applying unmerged commits
Unfortunately, not everything we code ends up in production. Many times, halfway through a feature, we realize it isn't needed or it's better done another way, so we usually delete the branch.
But what if in one of those commits we fixed a bug?
No problem, because git always keeps all commits, and even if you delete the branch you will still have access to that commit if you use its hash.
2.3 - Extra
Additionally, we can specify a range for cherry pick, but as I mentioned before, it’s very likely you’ll run into conflicts. Still, the syntax is as follows:
git cherry-pick <gitHash>..<gitHash>The command will cherry pick all the commits between the first and second hash.
3 - Running cherry pick from the command line
To run a cherry pick, you need to know the hash of the commit you want to apply. On GitHub, you can find it in the history on the right side.
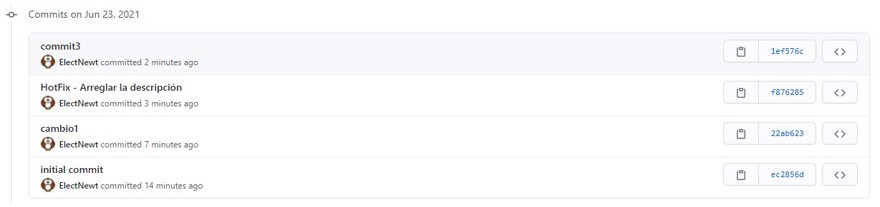
Note: you can also see the hash using git log on the command line.
The small code on the right is enough, but if you click copy you’ll see a longer code is copied, which also works.
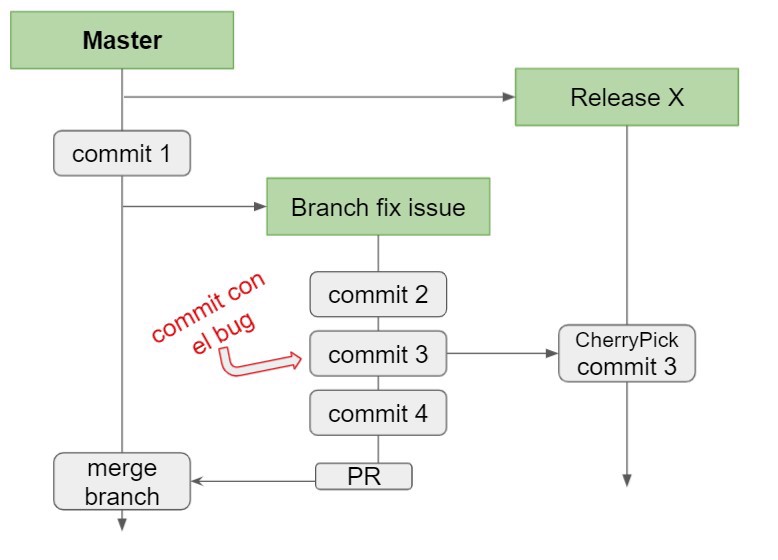
Our goal is to move the second commit from the (hotfix) branch to our release branch as seen in the image:
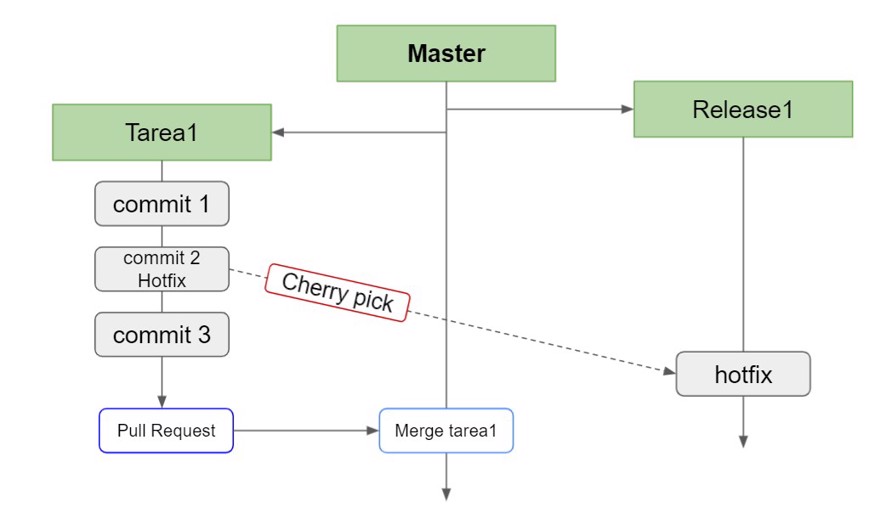
To do this, we have to switch to the release branch
git checkout release1And now enter the cherry pick command, remember to have the hash handy
git cherry-pick <hash>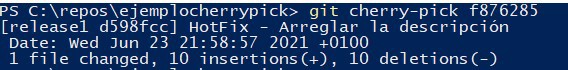
Finally, you have to run git push to send the changes to the server.
3.1 - Running cherry pick in GitHub Desktop
For a while now, I have been using the GitHub app for a git visual. There are other options like Gitkraken or Visual Studio extensions, but for me, GitHub Desktop is enough.
To cherry pick in GitHub Desktop, you need to be on the branch where the commit is, and then go to the history.
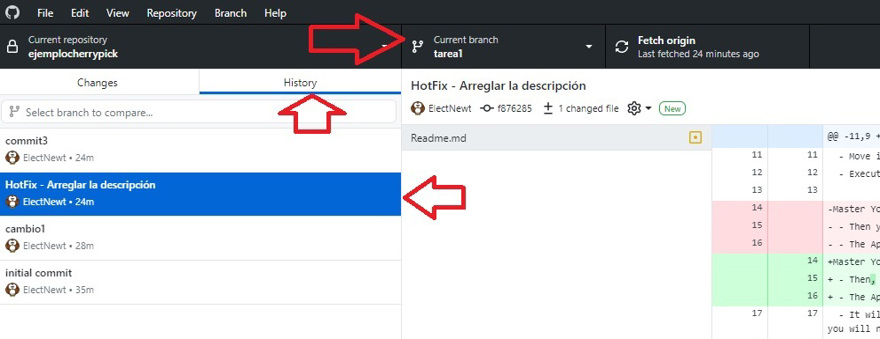
Then you must drag it with the left mouse button onto the branch where you want to apply it.
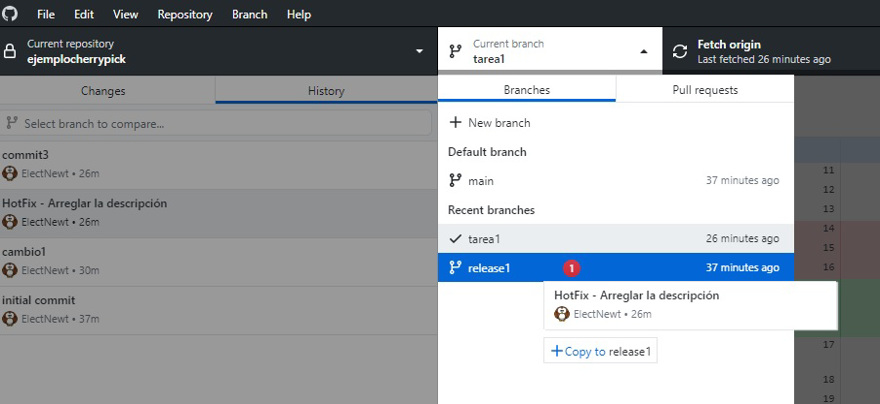
The UI will automatically switch to the branch where you applied the cherry pick and the push button will appear.
Conclusion
Cherry pick is a command that is very powerful in certain situations, but you should not use it as a replacement for merge or rebase.
Personally, I consider it an advanced git command since it requires knowledge of git commands in depth.
In this post we have seen:
- What cherry pick is in git.
- When to use cherry pick in git.
- How to run cherry pick from the command line and from the GitHub Desktop interface

