This post discusses how to use the "Database First" approach in Entity Framework Core. For those of you who are not familiar with Entity Framework, it is a Microsoft framework that makes database application development easier as we saw in one of our previous posts.
Index
1 - What is database first?
The Database First approach means you first create the database and then generate the Entity Framework Core model from it. This can be useful if you already have an existing database or if you want more control over the database structure.
2 - Implementing Database First with Entity Framework Core
Before we move on to the implementation itself, I want to mention that we’ll be using a MySQL database via Docker, but this approach works with any relational database. The only change, apart from differences in script syntax, is the connection string in the C# code.
The rest should be database agnostic.
First, let's create the database. In this case, it’s simple: a couple of tables with a relationship between them
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS `cursoEF`;
USE `cursoEF`;
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `userid` (
`UserId` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`UserName` varchar(50) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`UserId`),
UNIQUE KEY `UserName` (`UserName`)
);
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `wokringexperience` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`UserId` int(11) NOT NULL,
`Name` varchar(150) NOT NULL,
`Details` varchar(5000) NOT NULL,
`Environment` varchar(500) NOT NULL,
`StartDate` date DEFAULT NULL,
`EndDate` date DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
FOREIGN KEY (`UserId`) REFERENCES `userid`(`UserId`)
);And if you connect with a UI, this is what you should see:
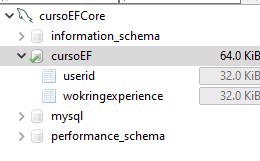
2.1 - Importing entities from a database with Entity Framework Core
To get started, first you need an existing application, in my case, it’s a Web API (available on GitHub), and you need to install the Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Design package.
You can add it manually, or with the following command:
dotnet add package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Design
In my particular case I use MySQL, so I also need to add the MySQL package:
dotnet add package MySql.EntityFrameworkCore
If you use another database like MariaDB or SQL Server, the packages you need to install are different, so I recommend checking the documentation.
Once the process is done, what we want is to import the database tables as entities, and to do that we run the Entity Framework Core scaffold command:
dotnet ef dbcontext scaffold "server=127.0.0.1;port=3306;database=cursoEF;user=cursoEFuser;password=cursoEFpass" MySql.EntityFrameworkCore -o ModelsIn my case I’m running it with the specified user, but you can use the connection string that matches your database.
Finally, the -o Models option indicates where the generated classes will be created.
When it finishes, you’ll see something like this:
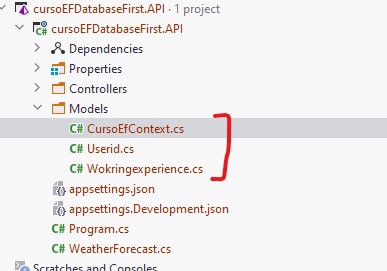
As you can see, it creates both the DBContext, representing the database, and a DBSet for each table.
For example, this is the entity generated to represent the userid table
public partial class Userid
{
public int UserId1 { get; set; }
public string UserName { get; set; } = null!;
public virtual ICollection<Wokringexperience> Wokringexperiences { get; } = new List<Wokringexperience>();
}
3 - Improving the default Entity Framework implementation
By default, the database connection is inside our DBContext and we need to change this because it isn’t secure, in fact, there’s a warning by default.
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder)
#warning To protect potentially sensitive information in your connection string, you should move it out of source code. You can avoid scaffolding the connection string by using the Name= syntax to read it from configuration - see https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=2131148. For more guidance on storing connection strings, see http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=723263.
=> optionsBuilder.UseMySQL("server=127.0.0.1;port=4306;database=cursoEF;user=cursoEFuser;password=cursoEFpass");
What we need to do is configure our DBContext inside our dependency container. Depending on your .NET version, this will be in either the startup.cs or program.cs class. Ideally, the connection string should be in the configuration file so you can use IConfiguration or, even better, in a credentials management vault. The code will look like this:
builder.Services.AddDbContext<CursoEfContext>(options =>
options.UseMySQL(builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("cursoEF")
?? throw new Exception("missing connectionstring")));
This allows us to remove the Onconfiguring method from our DBContext.
4 - C# application example with Entity Framework
Now we just need to try out the app. For this example I’ll write some simple code and run everything from the controller. If you’ve seen my channel, you know I never recommend doing this, but for a proof of concept it’s acceptable.
- My post on the structure of a C# application
But for this example, we’ll just create an endpoint to insert data:
[ApiController]
[Route("[controller]")]
public class CursoEFController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly CursoEfContext _context;
public CursoEFController(CursoEfContext context)
{
_context = context;
}
[HttpPost]
public async Task<int> AddUser(UserDto userDto)
{
Userid user = new Userid()
{
UserName = userDto.UserName
};
await _context.Userids.AddAsync(user);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return user.UserId1;
}
}
public record UserDto(string UserName);And here's the result:
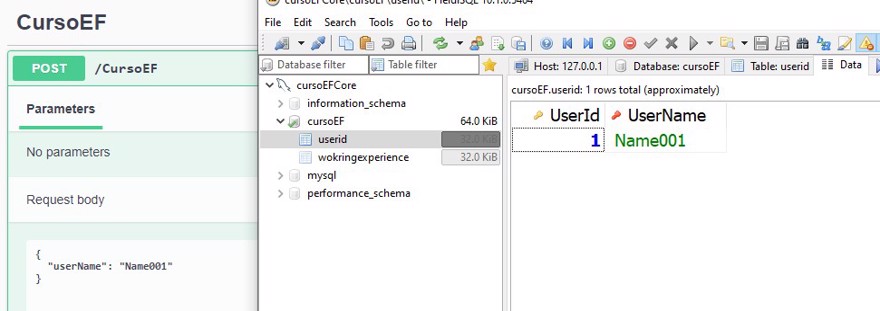
Remember that to perform CRUD operations you can use LINQ on the DBSet.
5 - Updating the model using Database First in EF Core
To update the model (that is, the C# classes inside our project) when the database structure is changed, we should run the same command we used for the initial execution, just adding the --force option
dotnet ef dbcontext scaffold "server=127.0.0.1;port=3306;database=cursoEF;user=cursoEFuser;password=cursoEFpass" MySql.EntityFrameworkCore -o Models --forceAnd with that we finish the Database First part, where you have the database already created when you start developing.


